Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block is a common procedure used in pain management to treat conditions such as complex regional pain syndrome and sympathetically mediated pain. It involves injecting medication into the sympathetic nerves located in the lower back to provide pain relief and improve functionality. Understanding the CPT code for this procedure is crucial for accurate billing and reimbursement. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block CPT Code, including its anatomy, procedure, coding, billing, and future trends.
Understanding Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block
Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block is a medical procedure that targets the sympathetic nerves running along the lumbar spine. These nerves play a crucial role in controlling blood flow and pain sensation in the lower extremities. By blocking these nerves, the procedure effectively interrupts the pain signals from reaching the brain, providing much-needed relief to patients suffering from chronic pain.
The Anatomy Involved
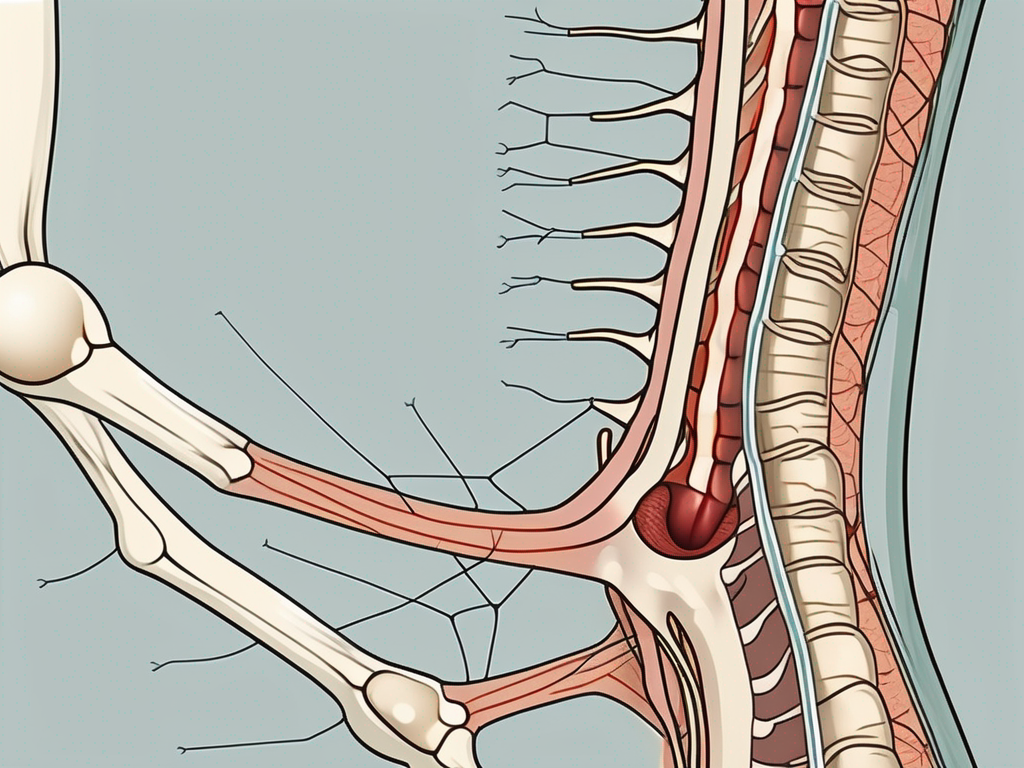
To fully grasp the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block procedure, it is essential to have a basic understanding of the relevant anatomy. The lumbar sympathetic chain consists of a series of interconnected ganglia located on either side of the spine. These ganglia act as relay stations, transmitting pain signals from the lower extremities to the brain. During the procedure, a needle is carefully inserted near the target ganglia, and a local anesthetic or neurolytic agent is injected to block the nerve impulses.
Each ganglion within the lumbar sympathetic chain has a specific function, contributing to the overall regulation of blood flow and pain perception. The ganglia work together to maintain a delicate balance in the body, ensuring proper circulation and pain management. By targeting these ganglia, the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block procedure aims to restore this balance and alleviate the debilitating pain experienced by patients.
The Procedure Explained
Prior to undergoing a Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block, patients are usually given detailed instructions and may be advised to abstain from food and drink for a certain period. This preparation helps ensure optimal conditions for the procedure and minimizes any potential complications. Additionally, patients may be asked to disclose any medications they are taking, as some drugs can interfere with the effectiveness of the nerve block.
The procedure is typically performed under fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance to ensure accurate needle placement. These imaging techniques provide real-time visualization of the spine, allowing the healthcare provider to precisely locate the target ganglia. This level of precision is crucial to the success of the procedure and helps minimize the risk of complications.
Once the patient is prepared, the needle is inserted near the desired ganglion. To confirm proper needle position, a contrast dye may be injected, which allows the healthcare provider to visualize the spread of the dye within the targeted area. This step ensures that the needle is accurately placed, increasing the chances of a successful nerve block.
Finally, the anesthetic or neurolytic agent is injected to temporarily or permanently block the nerves. Commonly used agents include phenol, alcohol, or radiofrequency energy. These substances work by disrupting the normal functioning of the nerves, effectively preventing them from transmitting pain signals to the brain.
Following the procedure, patients are typically monitored for a short period to ensure their safety and well-being. It is normal to experience some temporary numbness or weakness in the lower extremities after the nerve block. However, this usually subsides within a few hours, and patients can expect to experience significant pain relief in the days and weeks following the procedure.
In conclusion, Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block is a valuable medical procedure that targets the sympathetic nerves along the lumbar spine. By blocking these nerves, patients can find relief from chronic pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Decoding the CPT Code
The CPT code for Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block is essential for accurate coding and billing. Correctly coding this procedure not only ensures proper reimbursement but also helps in tracking treatment outcomes and contributing to research and analysis in pain management.
The Importance of Correct Coding
Accurate coding is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. With the correct CPT code, healthcare providers can communicate the specific procedure performed to insurance companies, facilitating reimbursement. Additionally, accurate coding helps in maintaining comprehensive patient medical records and supporting research in pain management.
When it comes to Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block, proper coding is of utmost importance. This procedure involves the injection of local anesthetic or neurolytic agents into the lumbar sympathetic ganglia to alleviate pain. By accurately coding this procedure, healthcare providers can ensure that they are appropriately compensated for their services, allowing them to continue providing high-quality care to their patients.
Moreover, correct coding plays a significant role in tracking treatment outcomes. By consistently using the correct CPT code for Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block, healthcare providers can gather data on the effectiveness of this procedure in managing pain. This information can then be analyzed to identify trends, evaluate patient satisfaction, and make informed decisions regarding treatment plans.
Breakdown of the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block CPT Code
The Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block CPT code falls under the category of “Interventional Pain Management Procedures.” The specific code may vary depending on factors such as the approach used (fluoroscopic or ultrasound-guided), the number of levels treated, and whether it is performed bilaterally.
When coding for Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block, healthcare providers must carefully consider the approach used during the procedure. Fluoroscopic guidance involves the use of real-time X-ray imaging to ensure accurate needle placement, while ultrasound-guided techniques utilize ultrasound technology to visualize the target area. The choice of approach may depend on factors such as patient anatomy, physician preference, and equipment availability.
Additionally, the number of levels treated during the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block procedure can impact the CPT code selection. The lumbar sympathetic ganglia are located on either side of the lumbar spine, and the procedure may involve targeting one or multiple levels. Proper documentation of the levels treated is crucial for accurate coding and billing.
Furthermore, healthcare providers must consider whether the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block is performed bilaterally, meaning both sides of the body are treated simultaneously. Bilateral procedures require specific coding considerations to ensure proper reimbursement and accurate representation of the services rendered.
It is important to consult the current version of the CPT code manual for the accurate code and any accompanying instructional notes. Proper documentation, including medical history, physical examination findings, and procedural details, is crucial for selecting the appropriate code.
In conclusion, accurate coding of the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block procedure is vital for healthcare providers, patients, and the field of pain management as a whole. By understanding the importance of correct coding, healthcare providers can ensure proper reimbursement, track treatment outcomes, and contribute to research and analysis in pain management.
Billing and Reimbursement for Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block
Accurate billing and reimbursement for Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block require a comprehensive understanding of the billing process, documentation requirements, and factors that may affect reimbursement.
Factors Affecting Reimbursement
Several factors can impact the reimbursement for Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block. Insurance coverage and policies, diagnosis codes, medical necessity, and proper documentation are all crucial in determining reimbursement rates. It is advisable to verify insurance coverage and pre-authorization requirements before the procedure to ensure smooth reimbursement.
Common Billing Errors to Avoid
To prevent billing errors and denials, healthcare providers should pay close attention to coding accuracy, documentation completeness, and adherence to insurance billing guidelines. Common errors include incorrect coding, inadequate documentation of medical necessity, and failure to demonstrate the procedure’s effectiveness or its impact on patient outcomes. Regular audits and staff training can help reduce billing errors and improve reimbursement rates.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block CPT Code
Patients and healthcare professionals often have questions regarding the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block CPT code. Let’s address a few of the most common queries:
What Does the CPT Code Include?
The Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block CPT code includes the procedural, diagnostic, and therapeutic elements necessary for successful treatment. The components typically include the injection of an anesthetic or neurolytic agent, the fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance, and any additional necessary procedures.
How Often Can This Procedure Be Billed?
The frequency of billing for Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block depends on several factors, including medical necessity, patient response to previous treatments, and insurance coverage. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate frequency and the necessity of repeat procedures.
Future Trends in Coding for Pain Management Procedures
The field of pain management is continuously evolving, and coding procedures must adapt to keep pace with advancements in technology and treatment options.
The Impact of Technology on Coding
New technological advancements, such as minimally invasive procedures, precision medicine, and real-time monitoring, are revolutionizing the field of pain management. As these technologies become more prevalent, coding and documentation guidelines will need to evolve accordingly to accurately capture the complexity and effectiveness of these procedures.
Predicted Changes in CPT Coding
With advancements in pain management techniques, it is anticipated that CPT coding for procedures like Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block will become more specific and refined. This will provide a clearer picture of the intricacies involved in these procedures and facilitate accurate billing and reimbursement.
In conclusion, understanding the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Block CPT code is crucial for healthcare professionals involved in pain management. By grasping the anatomy, procedure, coding, billing, and future trends related to this procedure, healthcare providers can ensure accurate documentation, billing, and reimbursement, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes. As always, it is advisable to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized medical advice and guidance.