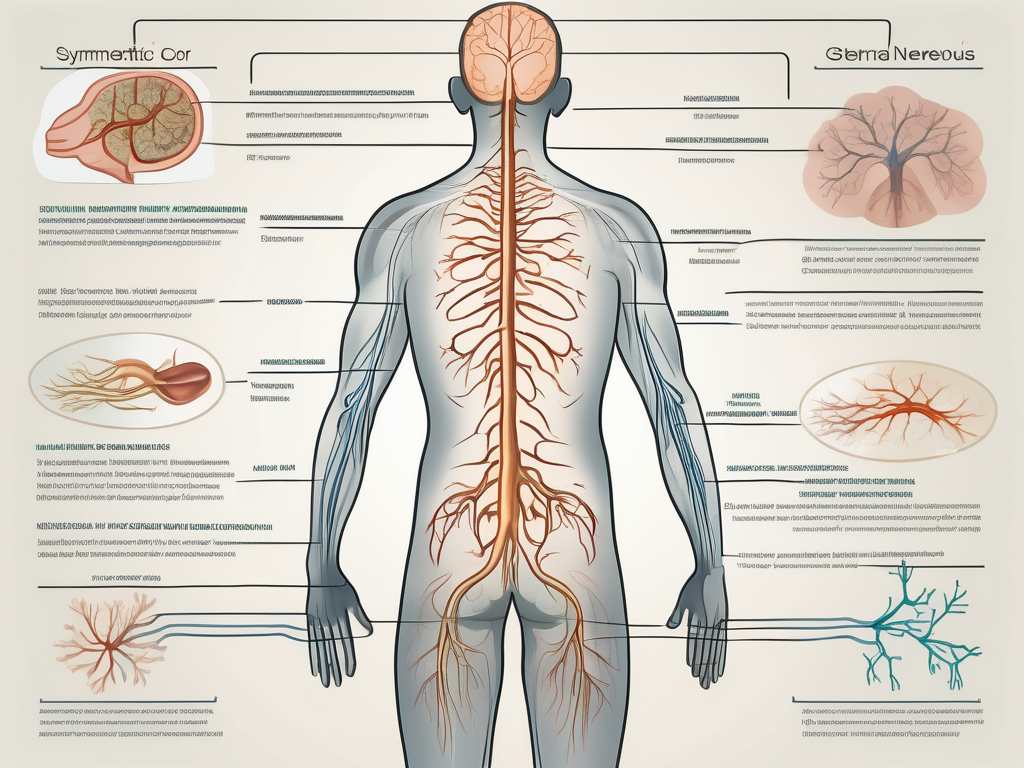
The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. It is a branch of the autonomic nervous system that helps regulate various bodily functions and respond to stressors. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the anatomy, functions, and disorders associated with the sympathetic nervous system. We will also delve into modern treatment approaches and discuss the future directions of research in this field.
Introduction to the Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network of neurons, neurotransmitters, and receptors that facilitate communication between different parts of the body. It can be broadly categorized into two main divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, which serve as the command center for the body. It receives and processes sensory information, initiates motor responses, and coordinates various bodily functions.
Imagine the central nervous system as the conductor of a grand symphony, directing each instrument to play its part in perfect harmony. It orchestrates the intricate dance of neurons, ensuring that messages are relayed accurately and efficiently throughout the body.
On the other hand, the peripheral nervous system encompasses all the nerves and ganglia outside the CNS. It connects the CNS to the rest of the body, allowing for the transmission of signals to and from various organs and tissues.
Think of the peripheral nervous system as the vast network of roads and highways that connect different cities and towns. It serves as the communication superhighway, enabling information to flow seamlessly between the central command center and the farthest reaches of the body.
Autonomic Nervous System: Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
The autonomic nervous system is a subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions. It can be further divided into two branches: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
The sympathetic nervous system is like a vigilant guardian, always on the lookout for potential threats. When faced with danger or stress, it triggers the “fight or flight” response, preparing the body for action. Heart rate increases, blood vessels constrict, and adrenaline surges through the bloodstream, readying the body to face any challenge.
On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system is the gentle caretaker, promoting relaxation and restoring the body to a state of rest and recovery. It slows down the heart rate, dilates blood vessels, and stimulates digestion, allowing the body to conserve energy and heal.
Imagine the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems as two sides of a coin, constantly working in harmony to maintain a delicate balance within the body. Like a skilled tightrope walker, they navigate the fine line between action and relaxation, ensuring that the body responds appropriately to its ever-changing environment.
Anatomy of the Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is a fascinating network of interconnected ganglia and neurons that extends throughout the body, working tirelessly to maintain balance and respond to various stimuli.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the intricate structure of this remarkable system.
The Sympathetic Chain Ganglia
The sympathetic chain ganglia, also known as the paravertebral ganglia, are like a string of pearls nestled alongside the spinal cord. These ganglia serve as crucial communication hubs, connecting the sympathetic nervous system to the target organs.
Within each ganglion, a bustling community of cells called ganglion cells resides. These cells eagerly receive signals from the preganglionic neurons and act as intermediaries, transmitting these signals to the postganglionic neurons. It’s like a relay race, with each cell passing the baton of information to the next.
Pre and Postganglionic Neurons
To keep the sympathetic nervous system running smoothly, it relies on two types of neurons: preganglionic and postganglionic neurons.
The preganglionic neurons, originating from the spinal cord, embark on a journey to reach the sympathetic chain ganglia. These brave neurons release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, igniting a spark of communication that sets the entire system in motion.
Once the signals have reached the ganglia, it’s time for the postganglionic neurons to take the stage. These neurons, extending from the ganglia to the target organs, are the messengers that deliver the vital instructions. They release the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, which acts as a key that unlocks specific receptors in the target organs, allowing for precise control over their functions.
Neurotransmitters Involved
While acetylcholine and norepinephrine are the stars of the show, the sympathetic nervous system boasts a diverse cast of neurotransmitters that contribute to its intricate dance.
Among these neurotransmitters is dopamine, a chemical messenger that plays a role in regulating movement, motivation, and reward. Then there’s epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, which surges through our veins during times of excitement or stress, preparing our bodies for action.
Last but not least, serotonin, often associated with mood regulation, also lends a helping hand to the sympathetic nervous system. This neurotransmitter influences various bodily functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and metabolism, contributing to our overall well-being.
So, next time you marvel at the wonders of the sympathetic nervous system, remember the intricate web of ganglia, the courageous preganglionic neurons, and the dedicated postganglionic messengers. It’s a symphony of neurotransmitters and neurons working harmoniously to keep our bodies in perfect balance.
Functions of the Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system performs a wide range of functions that are essential for our day-to-day survival and well-being.
While the fight or flight response is one of the key functions of the sympathetic nervous system, there are other fascinating roles it plays in our bodies.
The Fight or Flight Response
One of the key functions of the sympathetic nervous system is to initiate the fight or flight response. When faced with a perceived threat or stressor, the sympathetic nervous system releases a surge of hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones increase heart rate, dilate the airways, and redirect blood flow to the muscles, preparing the body for action.
This response is crucial for our survival, allowing us to effectively respond to dangerous situations and protect ourselves from harm.
Regulation of Body Temperature
The sympathetic nervous system also plays a role in regulating body temperature. When the body temperature rises, the sympathetic nervous system triggers sweating, which helps dissipate heat and cool the body down. Conversely, in cold temperatures, the sympathetic nervous system constricts blood vessels near the skin’s surface, reducing heat loss and preserving core body temperature.
Isn’t it amazing how our bodies have built-in mechanisms to maintain the perfect temperature for optimal functioning?
Control of Blood Pressure
The sympathetic nervous system is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. It can constrict or dilate blood vessels, depending on the body’s needs. By constricting blood vessels, the sympathetic nervous system can increase blood pressure and ensure an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to various organs and tissues.
Next time you feel your heart racing or your blood pressure rising, remember that it’s your sympathetic nervous system working diligently to keep your body in balance.
These are just a few examples of the incredible functions performed by the sympathetic nervous system. Its intricate control over our bodily processes is truly awe-inspiring and a testament to the complexity of the human body.
Disorders Associated with the Sympathetic Nervous System
While the sympathetic nervous system is vital for our well-being, its dysfunction can lead to a range of disorders. Understanding these disorders and their impact on our health is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Hypertension and the Sympathetic Nervous System
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is often associated with increased sympathetic nervous system activity. When the sympathetic nerves are overstimulated, blood vessels constrict, leading to elevated blood pressure levels. This continuous strain on the cardiovascular system can have detrimental effects on various organs, such as the heart, kidneys, and brain. Over time, it can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications.
Managing hypertension involves a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle modifications, medication, and stress reduction techniques. By targeting the overactivity of the sympathetic nervous system, healthcare professionals aim to restore a healthy balance and reduce the risk of complications.
Anxiety Disorders and the Sympathetic Nervous System
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. These disorders are characterized by excessive and persistent feelings of fear and worry, often accompanied by physical symptoms.
The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in the body’s response to stress and perceived threats. In individuals with anxiety disorders, the sympathetic nervous system can become overactivated, leading to heightened physiological responses. Increased heart rate, sweating, rapid breathing, and a sense of impending doom are common symptoms experienced during anxiety attacks.
Understanding the connection between anxiety disorders and the sympathetic nervous system is essential for developing effective treatment strategies. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication can help individuals manage their symptoms and regain control over their lives.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy refers to the damage or dysfunction of the autonomic nerves, including those of the sympathetic nervous system. This condition can have a wide range of symptoms and can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning.
Impaired blood pressure control is one of the hallmark symptoms of autonomic neuropathy. Fluctuations in blood pressure can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, and an increased risk of falls. Gastrointestinal disturbances, such as delayed stomach emptying and constipation, are also common in individuals with autonomic neuropathy.
Urinary problems, such as urinary retention or incontinence, can also occur due to the dysfunction of the sympathetic nerves that control bladder function. Additionally, autonomic neuropathy can lead to sexual dysfunction, including erectile dysfunction in men and decreased lubrication in women.
Various factors can contribute to the development of autonomic neuropathy, including diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications. Managing this condition involves addressing the underlying cause, controlling symptoms, and making lifestyle modifications to improve overall well-being.
By understanding the disorders associated with the sympathetic nervous system, healthcare professionals can provide targeted interventions to improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions. Ongoing research and advancements in treatment options continue to expand our knowledge and improve outcomes for patients.
The Sympathetic Nervous System and Modern Medicine
Advancements in medical science have allowed for the development of various treatment approaches targeting the sympathetic nervous system. This intricate network of nerves plays a crucial role in our body’s response to stress and emergencies, regulating functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and sweating.
Pharmacological Manipulation of the Sympathetic Nervous System
Pharmaceutical interventions can be used to modulate sympathetic nervous system activity. Doctors often prescribe drugs such as beta-blockers and alpha-blockers to regulate heart rate and blood pressure. These medications work by blocking the effects of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in activating the sympathetic nervous system, on specific receptors in the body.
However, the use of pharmacological agents is not limited to cardiovascular conditions. Recent studies have shown promising results in the treatment of anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder, by targeting the sympathetic nervous system. By modulating the activity of this system, these medications can help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from these conditions.
Surgical Interventions: Sympathectomy
In some cases, surgical interventions may be recommended to manage certain conditions associated with the sympathetic nervous system. Sympathectomy is a procedure that involves the removal or ablation of specific sympathetic nerves. It is commonly performed to treat excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) and certain vascular disorders.
Hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating, can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life. From social discomfort to difficulties in professional settings, this condition can be debilitating. Sympathectomy offers a potential solution by disrupting the signals responsible for excessive sweating. By selectively removing or ablating the sympathetic nerves responsible for this condition, patients can experience a significant reduction in sweating and regain their confidence.
Future Directions in Research and Treatment
As our understanding of the sympathetic nervous system continues to evolve, ongoing research aims to uncover new treatment modalities and improve existing therapies. Novel pharmacological agents and targeted interventions hold promise in the management of disorders related to sympathetic nervous system dysfunction.
Researchers are exploring the potential of gene therapy to modulate the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. By targeting specific genes involved in the regulation of sympathetic nerve activity, scientists hope to develop more precise and effective treatments for conditions such as hypertension and heart failure. This cutting-edge approach could revolutionize the field of medicine and provide new hope for patients with sympathetic nervous system disorders.
Additionally, advancements in neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), are enabling researchers to visualize and map the activity of the sympathetic nervous system in real-time. This valuable information can help identify abnormalities and guide the development of personalized treatment plans.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Sympathetic Nervous System
In conclusion, the sympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. It helps regulate various bodily functions, prepares us for fight or flight responses, and ensures proper blood pressure and temperature control. However, when the sympathetic nervous system becomes dysregulated, it can lead to disorders such as hypertension, anxiety disorders, and autonomic neuropathy. Advances in modern medicine offer pharmacological and surgical interventions to manage these conditions, with ongoing research aiming to develop new treatment approaches. Understanding the role of the sympathetic nervous system is crucial for optimizing our health and improving patient outcomes.
By staying informed about the latest research and advancements in this field, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat disorders associated with the sympathetic nervous system, ultimately improving the lives of their patients.