Living with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) in the foot can be a challenging and debilitating experience. The constant pain and discomfort make it difficult to perform even simple daily activities. Thankfully, there are treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition. One promising treatment option for CRPS in the foot is a Sympathetic Nerve Block.
Understanding CRPS and Its Impact on the Foot
Defining CRPS: A Brief Overview
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, commonly referred to as CRPS, is a chronic and progressive condition characterized by severe pain, swelling, and changes in the skin. It typically affects an extremity, such as the foot, and its exact cause is still not fully understood. CRPS can occur after an injury, surgery, or even without any apparent trigger.
CRPS is a complex condition that involves dysfunction of the nervous system, particularly the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including blood flow, temperature, and pain perception. In CRPS, there is an abnormal response of the sympathetic nervous system, leading to the characteristic symptoms.
How CRPS Affects the Foot
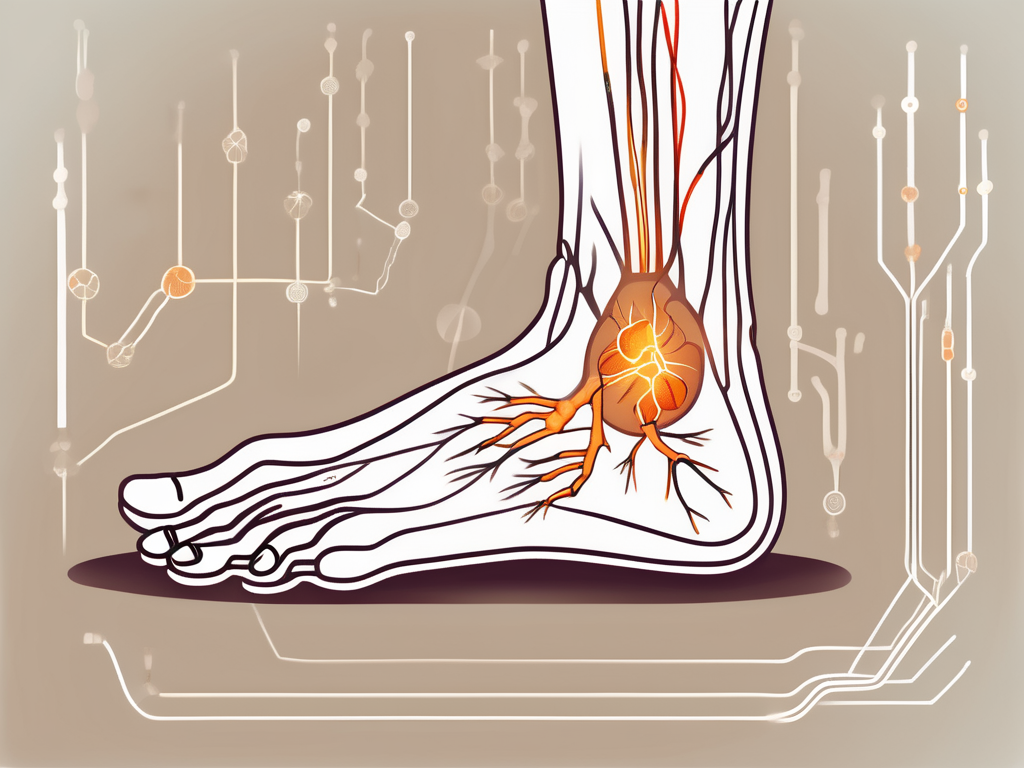
When CRPS affects the foot, it can lead to significant impairment in mobility and function. The pain can range from mild to excruciating, making it difficult to bear weight or walk. Swelling and changes in skin temperature and color may also be present. These symptoms can have a profound impact on the individual’s ability to perform daily activities and adversely affect their overall quality of life.
The pain experienced in CRPS is often described as burning, throbbing, or shooting. It may be accompanied by hypersensitivity to touch or even the slightest movement. This heightened sensitivity, known as allodynia, can make it challenging to wear shoes or socks, as even the gentlest pressure can trigger intense pain.
In addition to the physical symptoms, CRPS can also have psychological and emotional effects. The constant pain and limitations in mobility can lead to feelings of frustration, helplessness, and depression. The individual may struggle with the loss of independence and the inability to engage in activities they once enjoyed.
Furthermore, CRPS can have a significant impact on the individual’s social life and relationships. The constant pain and physical limitations may make it difficult to participate in social gatherings or engage in hobbies and recreational activities. This can lead to feelings of isolation and a sense of being misunderstood by others.
It is important for individuals with CRPS to receive comprehensive and multidisciplinary care. Treatment may involve a combination of medication, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and psychological support. The goal is to manage pain, improve function, and enhance the individual’s overall well-being.
In conclusion, CRPS is a complex condition that can have a profound impact on the foot and the individual’s quality of life. The pain, swelling, and changes in skin associated with CRPS can lead to significant mobility impairments and emotional distress. It is crucial for individuals with CRPS to seek appropriate medical care and support to effectively manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
The Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System in CRPS
The Sympathetic Nervous System Explained
The sympathetic nervous system is a part of our autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. It works in conjunction with the parasympathetic nervous system to regulate various bodily functions, including blood pressure, heart rate, and sweating.
The sympathetic nervous system is like a vigilant guardian, constantly monitoring our environment and responding to potential threats or stressors. When faced with a perceived danger, it triggers the “fight or flight” response, preparing our body for action. This response involves the release of stress hormones, such as adrenaline, which increase heart rate, dilate blood vessels, and redirect blood flow to the muscles, preparing us to either confront the threat or escape from it.
Connection between the Sympathetic Nervous System and CRPS
In CRPS, the sympathetic nervous system becomes overactive and can contribute to the persistent pain and inflammation observed in the affected foot. This overactivity may be caused by abnormal signaling from damaged or malfunctioning nerves in the limb. The sympathetic nerves, which normally help regulate blood flow and temperature, become hypersensitive and can cause blood vessels to constrict excessively, leading to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to the affected area.
Furthermore, the overactive sympathetic nervous system can trigger a cascade of inflammatory responses, releasing pro-inflammatory molecules that further exacerbate pain and inflammation. This vicious cycle of sympathetic overactivity and inflammation creates a self-perpetuating loop, making CRPS a challenging condition to manage.
Understanding the role of the sympathetic nervous system in CRPS has led to the development of various treatment approaches. One such approach is the use of sympathetic nerve blocks. These blocks involve the injection of local anesthetics or medications directly into the sympathetic ganglia or nerves to interrupt the faulty signaling and provide relief from the debilitating symptoms of CRPS.
While sympathetic nerve blocks can provide temporary relief, they are often used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes physical therapy, medication management, and psychological support. By addressing the overactive sympathetic nervous system, healthcare professionals aim to restore balance and improve the overall functioning of the affected limb.
Sympathetic Nerve Block: An Introduction
What is a Sympathetic Nerve Block?
A sympathetic nerve block is a minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting medication, such as a local anesthetic or a steroid, near the sympathetic nerves responsible for the abnormal pain signaling in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). This condition, also known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD), is a chronic pain disorder characterized by intense and prolonged pain, usually in the extremities.
The sympathetic nerves, part of the autonomic nervous system, play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including blood flow, temperature, and pain perception. In CRPS, these nerves become overactive, causing persistent pain and inflammation in the affected area. A sympathetic nerve block aims to interrupt this abnormal signaling and provide relief to the patient.
The Procedure of Sympathetic Nerve Block
The procedure typically takes place in an outpatient setting, such as a pain management clinic or a hospital. Before the nerve block, the patient will undergo a thorough evaluation, including a medical history review and physical examination. This assessment helps the specialist determine the most appropriate approach for the nerve block and ensures the patient’s safety.
During the procedure, the patient will be positioned comfortably, and the specialist will use imaging techniques like fluoroscopy or ultrasound to guide the needle placement. These imaging tools allow for precise targeting of the affected nerves, minimizing the risk of complications and maximizing the effectiveness of the nerve block.
Once the target area is identified, the specialist will cleanse the skin and apply a local anesthetic to numb the injection site. This helps minimize any discomfort during the procedure. Using a thin needle, the specialist will then carefully insert it near the affected nerves and administer the medication.
The medication used in a sympathetic nerve block can vary depending on the patient’s specific condition and the specialist’s preference. Local anesthetics, such as lidocaine or bupivacaine, are commonly used to provide immediate pain relief. These medications work by blocking the transmission of pain signals from the nerves to the brain.
In some cases, a steroid medication, such as cortisone, may be added to the local anesthetic. Steroids have potent anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce swelling and inflammation in the affected area. This combination of local anesthetic and steroid can provide both immediate and long-lasting relief for patients with CRPS.
After the medication is administered, the specialist will carefully remove the needle and apply a bandage to the injection site. The patient will then be monitored for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications or adverse reactions to the procedure.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness and duration of pain relief can vary from patient to patient. Some individuals may experience immediate relief, while others may require multiple nerve block procedures to achieve the desired outcome. The specialist will work closely with the patient to develop an individualized treatment plan and monitor their progress over time.
Sympathetic Nerve Block as a Treatment for CRPS in the Foot
The Science Behind the Treatment
The exact mechanisms by which a sympathetic nerve block provides pain relief in CRPS are still being studied. It is believed that the injected medication blocks the abnormal pain signals sent by the sympathetic nerves, effectively resetting the pain-processing system in the foot. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of some medications used in the block can help reduce swelling and improve overall function.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Sympathetic nerve blocks have shown promising results in managing the symptoms of CRPS in the foot for many individuals. The procedure has the potential to provide significant pain relief, improve mobility, and enhance the overall quality of life. However, it is important to note that like any medical procedure, sympathetic nerve blocks also carry some risks, including infection, bleeding, and nerve damage. It is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare professional before deciding on this treatment option.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Sympathetic Nerve Block for CRPS
Current Research Findings
A growing body of research is investigating the effectiveness of sympathetic nerve block as a treatment option for CRPS in the foot. While initial studies have shown promising results, more research and clinical trials are needed to establish its long-term effectiveness and determine the ideal candidates for this procedure. Consulting with a healthcare professional who specializes in pain management can provide valuable insights into the latest research findings and their implications.
Patient Outcomes and Satisfaction
Individual experiences with sympathetic nerve block for CRPS in the foot can vary. Some individuals may experience substantial pain relief and improved function, while others may have a more modest response. It is important to approach this treatment option with realistic expectations and understand that it may not work the same way for everyone. Speaking with individuals who have undergone this procedure and hearing about their personal experiences can provide additional insight.
Living with CRPS in the foot can be challenging, but by exploring treatment options like the sympathetic nerve block, individuals may find relief from their symptoms and regain control over their lives. It is crucial to have an open and honest discussion with a healthcare professional to determine if this treatment option is suitable and appropriate for one’s specific condition. Together, with the guidance of experienced medical professionals, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their treatment approach and embark on a path toward improved quality of life.