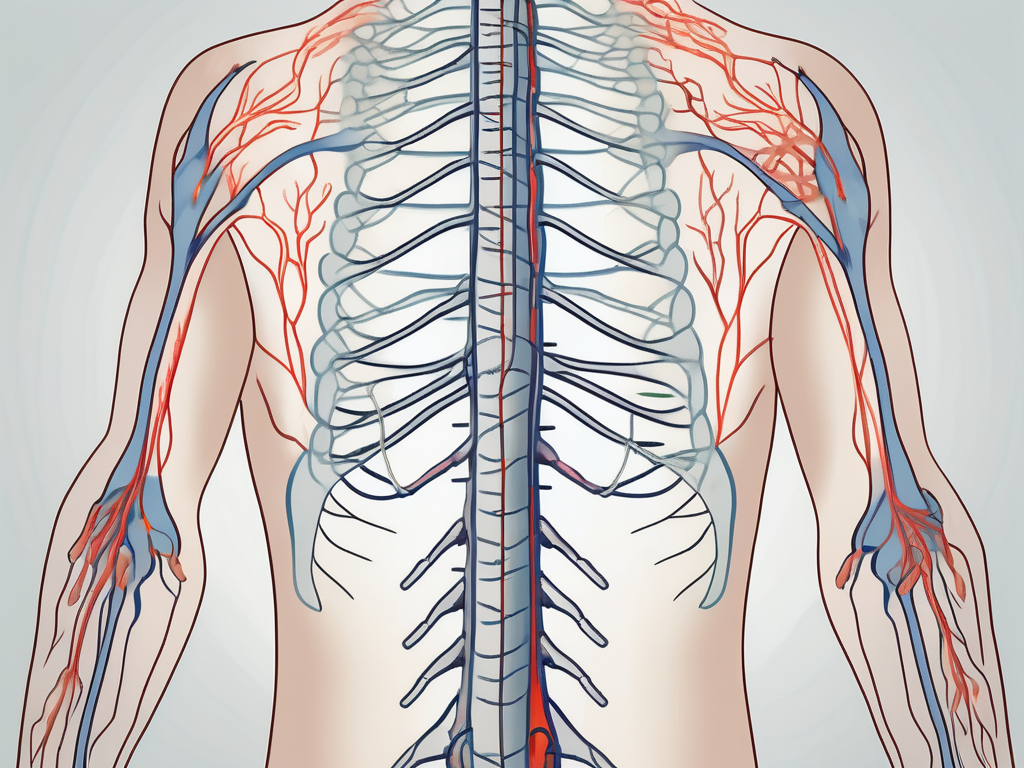
The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in our body’s ability to respond to various stimuli and maintain homeostasis. Understanding the intricate workings of this system is essential for comprehending the complexity of human physiology. This comprehensive overview aims to delve into the function, anatomy, and disorders related to the sympathetic nervous system while highlighting the latest research trends and future implications.
Understanding the Nervous System
The nervous system is an intricate network of specialized cells, known as neurons, that transmit electrochemical signals throughout the body. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling bodily functions. The nervous system can be divided into two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The Role of the Nervous System in the Human Body
The nervous system serves as the communication highway, relaying messages between different parts of the body. It facilitates voluntary actions, such as movement, as well as involuntary processes, such as breathing and digestion. Additionally, the nervous system plays a critical role in receiving and interpreting sensory information.
Differentiating Between the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system comprises all the nerves that extend from the CNS to the rest of the body. The sympathetic nervous system is one of two subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system, a component of the peripheral nervous system.
Let’s delve deeper into the central nervous system. The brain, which is the command center of the nervous system, is a complex organ that weighs about three pounds and is made up of billions of neurons. It is responsible for processing information, controlling thoughts and emotions, and coordinating various bodily functions. The brain can be divided into different regions, each with its own specialized functions. For example, the frontal lobe is involved in decision-making and problem-solving, while the occipital lobe is responsible for processing visual information.
Now, let’s shift our focus to the peripheral nervous system. This intricate network of nerves extends throughout the body, connecting the central nervous system to the various organs, muscles, and tissues. The peripheral nervous system can be further divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements, allowing us to consciously move our limbs or speak. On the other hand, the autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary processes, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
Within the autonomic nervous system, we find the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body’s response to stress or danger, often referred to as the “fight or flight” response. It increases heart rate, dilates blood vessels, and releases stress hormones, preparing the body for action. In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and restoration. It slows heart rate, constricts blood vessels, and conserves energy.
Delving into the Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is a fascinating and intricate network within our bodies that plays a crucial role in our response to stress and threatening situations. Known as the “fight or flight” response, it is a mechanism that prepares our body for action when faced with danger. Let’s explore this incredible system in more detail.
The Anatomy of the Sympathetic Nervous System
At the core of the sympathetic nervous system lies a chain of ganglia, which are clusters of nerve cell bodies, located on both sides of the spinal cord. These ganglia are interconnected by nerve fibers that extend throughout our body, forming an intricate web of communication. This network allows for the rapid transmission of nerve impulses to different target organs, ensuring a swift and coordinated response to potential threats.
Imagine this network as a well-coordinated team, with each ganglion acting as a vital player. They work together seamlessly, passing along crucial information and instructions to keep our body in sync and ready to face any challenge that comes our way.
The Neurotransmitters Involved in the Sympathetic Nervous System
Within the sympathetic nervous system, two primary neurotransmitters take center stage: norepinephrine and epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. These chemical messengers play a pivotal role in transmitting signals from nerve cells to target organs, triggering the appropriate response to stress or danger.
Think of norepinephrine and epinephrine as the conductors of an orchestra, guiding and coordinating the various instruments within our body. When stress or danger is detected, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors in target organs, setting off a cascade of physiological changes. Heart rate increases, blood vessels dilate, and various organs are activated, all in preparation for the potential physical demands that lie ahead.
It’s truly remarkable how our body’s intricate systems work together to ensure our survival. The sympathetic nervous system is just one example of the incredible complexity that exists within us. As we continue to explore the wonders of our bodies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable design and functionality that allows us to adapt and thrive in a world full of challenges.
The Functions of the Sympathetic Nervous System
One of the key functions of the sympathetic nervous system is the initiation of the fight or flight response. In situations that require immediate action, such as encountering a predator, the sympathetic nervous system activates various physiological changes to enhance survival.
But what exactly happens when the sympathetic nervous system kicks into gear? Let’s take a closer look.
The Sympathetic Nervous System and the Fight or Flight Response
When faced with a threat, the sympathetic nervous system triggers the release of stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones surge through our bloodstream, preparing our bodies for action.
As the heart rate increases, blood vessels constrict in non-essential areas, redirecting blood flow to the muscles. This ensures that our muscles receive an ample supply of oxygen and nutrients, enabling a rapid physical reaction. Our senses become heightened, allowing us to be more alert and responsive to our surroundings.
But that’s not all. The sympathetic nervous system also causes our airways to dilate, increasing the amount of oxygen we can take in. This extra oxygen fuels our muscles, providing them with the energy they need to fight or flee.
The Sympathetic Nervous System’s Role in Homeostasis
In addition to the fight or flight response, the sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, the body’s internal balance.
While it may seem contradictory, the sympathetic nervous system actually helps regulate vital functions such as blood pressure, body temperature, and digestion. It does so by adjusting the activity of various organs and systems in response to changing conditions.
For example, when we are in a stressful situation, the sympathetic nervous system increases blood pressure by constricting blood vessels. This ensures that our organs and tissues receive an adequate blood supply, even when we are under duress.
Furthermore, the sympathetic nervous system helps regulate body temperature by activating sweat glands and causing blood vessels near the skin’s surface to dilate. This allows excess heat to be released, helping to cool down the body.
When it comes to digestion, the sympathetic nervous system slows down processes such as stomach contractions and saliva production. This redirection of energy away from digestion allows our bodies to focus on more immediate needs, such as fighting or fleeing.
So, while the fight or flight response may be the most well-known function of the sympathetic nervous system, it is clear that this intricate network of nerves serves a much broader purpose in maintaining our overall well-being.
Disorders Related to the Sympathetic Nervous System
Despite its crucial role in our body, the sympathetic nervous system may also be associated with various disorders that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
The sympathetic nervous system, also known as the “fight or flight” response, is responsible for preparing our body to respond to stressful situations. However, when this system becomes dysregulated, it can lead to a range of disorders that affect different aspects of our health.
Common Disorders of the Sympathetic Nervous System
Some of the commonly observed disorders of the sympathetic nervous system include excessive sweating, hypertension (high blood pressure), and complex regional pain syndrome. These conditions can be debilitating and require specialized medical attention.
Excessive sweating, known as hyperhidrosis, can be a distressing condition that affects a person’s social and emotional well-being. It can lead to embarrassment and self-consciousness, making everyday activities challenging. Individuals with hyperhidrosis may find it difficult to shake hands, hold objects, or even wear certain types of clothing.
Hypertension, on the other hand, is a condition characterized by persistently high blood pressure. It can put a strain on the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health complications. Managing hypertension often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise, along with medication prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic pain condition that usually affects an arm or a leg. It is believed to be caused by a malfunction in the sympathetic nervous system, leading to persistent pain, swelling, and changes in skin temperature and color. CRPS can significantly impact a person’s ability to perform daily activities and may require a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, involving pain management specialists, physical therapists, and psychologists.
Treatment and Management of Sympathetic Nervous System Disorders
Treatment approaches for sympathetic nervous system disorders vary depending on the specific condition. Medications, lifestyle modifications, and therapy techniques such as nerve blocks or physical therapy may be utilized to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
For individuals with excessive sweating, treatment options may include antiperspirants, medications, or procedures such as Botox injections or surgical interventions. Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers like spicy foods or stressful situations, can also help manage symptoms.
In the case of hypertension, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing the condition. These changes may include adopting a low-sodium diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing stress through relaxation techniques or meditation. Medications, such as beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors, may also be prescribed to help control blood pressure.
Complex regional pain syndrome often requires a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. This may involve a combination of medications to manage pain, physical therapy to improve mobility and function, and psychological interventions to address the emotional impact of living with chronic pain. Nerve blocks, which involve injecting medication into or around the affected nerves, can also provide temporary relief for some individuals.
It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms related to the sympathetic nervous system to seek medical attention and work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan. With proper management, many of these disorders can be effectively controlled, allowing individuals to regain control of their lives and improve their overall well-being.
The Sympathetic Nervous System and Modern Research
Ongoing research in the field of sympathetic nervous system studies continues to illuminate the intricate workings of this complex system. The sympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “fight or flight” response, plays a crucial role in our body’s response to stress and danger. It is responsible for mobilizing our energy resources, increasing heart rate, and dilating blood vessels to prepare us for action.
Scientists are exploring the role of the sympathetic nervous system in various diseases and conditions. Investigations into its influence on cardiovascular health have revealed that chronic activation of the sympathetic nervous system can contribute to the development of hypertension, a major risk factor for heart disease. Additionally, studies have shown that the sympathetic nervous system may play a role in mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. Understanding the intricate relationship between the sympathetic nervous system and these conditions could pave the way for more effective treatments.
Furthermore, research has also focused on the link between the sympathetic nervous system and metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes. It has been found that chronic activation of the sympathetic nervous system can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to insulin resistance and abnormal glucose regulation. By unraveling the mechanisms behind this connection, scientists hope to develop targeted therapies that can restore metabolic balance and improve overall health.
Future Implications of Sympathetic Nervous System Research
As our understanding of the sympathetic nervous system deepens, its potential for future therapeutic approaches becomes increasingly apparent. Targeted treatments that modulate sympathetic activity could have profound implications for a wide range of conditions, ultimately improving patient outcomes. For example, medications that selectively block the sympathetic nervous system could be developed to lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension, while drugs that enhance sympathetic activity could be used to combat fatigue and improve energy levels in certain medical conditions.
Bringing together knowledge from the realms of anatomy, physiology, and research, this comprehensive overview has shed light on the function of the sympathetic nervous system. From the fight or flight response to the management of disorders, the sympathetic nervous system shapes our lives in numerous ways. Continued research in this field promises a better understanding of human physiology and potential interventions to improve health and well-being.
With the advancements in technology and the collaborative efforts of scientists worldwide, the future of sympathetic nervous system research looks promising. By delving deeper into the intricate workings of this complex system, we can uncover new insights and develop innovative treatments that could revolutionize healthcare. The potential impact of this research extends beyond the realm of medicine, as a better understanding of the sympathetic nervous system could also have implications in fields such as psychology and sports performance.