The sympathetic nervous system is a vital component of the human body’s autonomic nervous system. This guide aims to provide comprehensive information regarding the location, function, and disorders associated with the sympathetic nervous system. Understanding this complex system is essential for anyone interested in the intricacies of human physiology.
Understanding the Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body’s involuntary functions under stressful situations. It works in tandem with the parasympathetic nervous system, which controls the body’s rest and digestion responses. By understanding the roles and functions of the sympathetic nervous system, we can comprehend its significance in maintaining homeostasis.
The Role and Function of the Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in the body’s fight-or-flight response. When faced with a perceived threat, the sympathetic nervous system quickly springs into action, preparing the body for physical exertion. These responses include increased heart rate, dilation of the airways, and the release of stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol.
But did you know that the sympathetic nervous system doesn’t just affect our physical responses? It also influences our emotional state. When we experience fear or anxiety, the sympathetic nervous system activates, triggering a cascade of physiological changes that can intensify our emotions. This connection between the sympathetic nervous system and our emotional well-being highlights the intricate interplay between our mind and body.
The sympathetic nervous system also regulates various bodily functions such as blood pressure, digestion, and pupil dilation. Understanding how these functions are controlled is essential to appreciate the widespread impact of this intricate system.
The Structure of the Sympathetic Nervous System
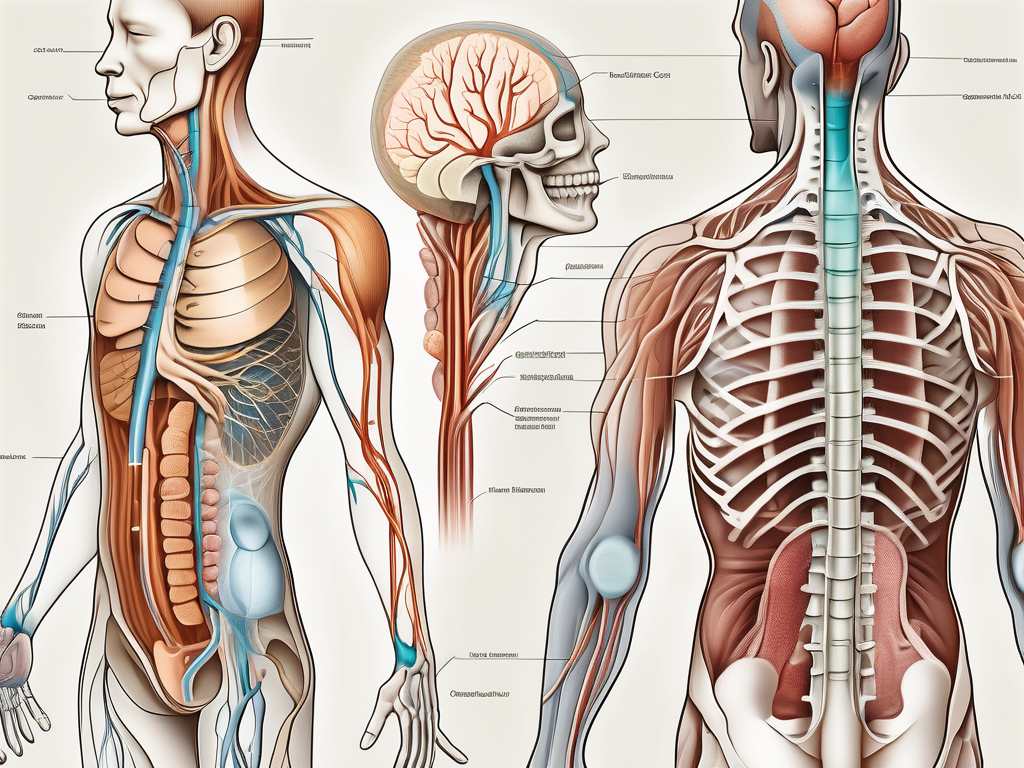
The sympathetic nervous system comprises a complex network of nerves, ganglia, and neurotransmitters. The sympathetic chain, a series of interconnected ganglia, runs parallel to the spinal cord. This positioning ensures efficient communication between the central nervous system and targets throughout the body.
Within the sympathetic chain, neurons release neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine that bind to specific receptors on target tissues. These receptors then elicit various responses, allowing the sympathetic nervous system to fine-tune its effects on different organs and systems.
Interestingly, the sympathetic nervous system doesn’t act alone. It collaborates with other parts of the body, such as the adrenal glands, to amplify its responses. The adrenal glands release additional stress hormones, further enhancing the sympathetic nervous system’s effects. This intricate coordination showcases the complexity and adaptability of our body’s stress response system.
Locating the Sympathetic Nervous System
Understanding the physical location of the sympathetic nervous system is vital to grasp its connection to the rest of the body.
The Sympathetic Chain and Its Location
The sympathetic chain, also known as the paravertebral ganglia, is a key component of the sympathetic nervous system. It is situated adjacent to the vertebral column, running from the base of the skull down to the coccyx. This location enables efficient and rapid communication with effector organs.
Imagine this intricate network of interconnected ganglia, resembling a chain of pearls, delicately nestled alongside the protective vertebral column. The sympathetic chain acts as a vigilant guardian, ready to relay important nerve signals to various regions of the body at a moment’s notice.
As the sympathetic chain extends its reach from the base of the skull to the coccyx, it forms a continuous pathway, allowing for seamless coordination of responses across different regions of the body. This interconnectedness ensures that the sympathetic nervous system can swiftly and effectively respond to various stimuli.
The Connection to the Spinal Cord
The sympathetic chain is closely intertwined with the spinal cord. Preganglionic sympathetic neurons originate in the spinal cord, specifically the thoracic and lumbar regions, before synapsing with postganglionic neurons within the sympathetic chain.
Picture the intricate dance between the spinal cord and the sympathetic chain, as they work in perfect harmony to transmit vital information throughout the body. The spinal cord, like a conductor, orchestrates the symphony of signals, while the sympathetic chain acts as the ensemble, relaying these messages to their intended destinations.
Understanding the connection between the spinal cord and the sympathetic chain is crucial for comprehending the extensive reach of the sympathetic nervous system throughout the body. It is through this intricate connection that the sympathetic nervous system can effectively regulate various physiological processes, ensuring our bodies can respond appropriately to different situations.
The Sympathetic Nervous System and the Body
The sympathetic nervous system has a profound impact on various organs and bodily functions. By exploring its influence, we can gain a deeper understanding of its systemic effects.
The Sympathetic Nervous System’s Impact on Organs
One of the primary functions of the sympathetic nervous system is to regulate the behavior of specific organs. For instance, it increases heart rate and widens blood vessels to ensure adequate blood supply during times of heightened activity or stress. This increased blood flow not only delivers oxygen and nutrients to the muscles but also helps remove waste products efficiently, optimizing performance.
Moreover, the sympathetic nervous system stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, providing an energy boost when needed. This glucose serves as fuel for the body, allowing individuals to respond quickly and effectively to demanding situations.
Additionally, the sympathetic nervous system dilates the pupils to enhance visual acuity, allowing individuals to perceive their surroundings with greater clarity. This heightened visual perception can be crucial in high-stress situations where quick reactions are necessary for survival.
Furthermore, the sympathetic nervous system speeds up breathing, increasing the oxygen intake and carbon dioxide elimination. This respiratory response ensures that the body receives an adequate supply of oxygen, which is vital for maintaining optimal cellular function and overall performance.
Lastly, the sympathetic nervous system shifts blood flow to the skeletal muscles, preparing the body for action. This redistribution of blood ensures that the muscles receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients, enabling individuals to perform physical tasks with strength and agility.
The Sympathetic Nervous System’s Role in Stress Response
Stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, prompting the release of stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones prepare the body to face potential threats, ensuring survival in dangerous situations.
However, chronic activation of the sympathetic nervous system due to persistent stress can lead to detrimental effects on overall well-being. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones can disrupt sleep patterns, impair immune function, and contribute to the development of various health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases and mental health disorders.
Understanding the role of stress in sympathetic nervous system activation is crucial for managing stress-related disorders effectively. By implementing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, exercise, and social support, individuals can help regulate their sympathetic nervous system activity, promoting better physical and mental health.
Disorders Related to the Sympathetic Nervous System
Various disorders can affect the normal functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. Recognizing these conditions and understanding their symptoms and management strategies is vital for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking help.
The sympathetic nervous system, also known as the “fight or flight” response, plays a crucial role in our body’s response to stress and danger. However, when this system malfunctions, it can lead to a range of disorders that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Common Disorders and Their Symptoms
While the sympathetic nervous system is crucial for overall well-being, its dysfunction can result in several disorders. These disorders may manifest as excessive sweating, high blood pressure, or abnormalities in heart rate. However, it’s important to note that the symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific disorder and the individual.
One common disorder related to the sympathetic nervous system is hyperhidrosis, which is characterized by excessive sweating. This condition can be extremely distressing and can significantly impact a person’s social and professional life. Another disorder is hypertension, or high blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, disorders such as tachycardia (rapid heart rate) and arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can also be attributed to sympathetic nervous system dysfunction.
Treatment and Management of Sympathetic Nervous System Disorders
Managing disorders related to the sympathetic nervous system involves addressing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms. Treatment options can range from pharmacological interventions to lifestyle modifications. For example, medications such as beta-blockers may be prescribed to regulate heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as stress management techniques, regular exercise, and a healthy diet can also help in managing these disorders.
Early diagnosis and proper management are crucial for ensuring optimal patient outcomes. Seeking medical attention at the first sign of symptoms is essential to prevent further complications and improve the overall quality of life for individuals affected by these disorders. Healthcare professionals play a vital role in educating patients about the importance of early intervention and providing them with the necessary tools and resources to manage their condition effectively.
The Future of Sympathetic Nervous System Research
Ongoing research into the sympathetic nervous system continues to shed light on its complex functioning and potential breakthroughs in treatment methods.
Current Research Trends
Scientists are actively investigating the role of the sympathetic nervous system in various physiological processes, including metabolism, inflammation, and cardiovascular health. Understanding these associations may open new avenues for developing targeted therapeutic interventions.
One intriguing area of current research is the connection between the sympathetic nervous system and mental health. Recent studies have suggested that dysregulation of the sympathetic nervous system may contribute to the development and progression of mental disorders such as anxiety and depression. By unraveling the intricate relationship between the sympathetic nervous system and mental health, researchers hope to develop innovative treatment approaches that could significantly improve the lives of individuals struggling with these conditions.
Potential Breakthroughs and Their Implications
Emerging research may lead to significant breakthroughs in treating disorders associated with the sympathetic nervous system. These breakthroughs could potentially enhance patient care, improve quality of life, and offer hope to individuals grappling with sympathetic nervous system disorders.
One potential breakthrough lies in the development of novel pharmacological agents that specifically target the sympathetic nervous system. By designing drugs that selectively modulate the activity of this system, researchers aim to minimize side effects and maximize therapeutic efficacy. Such advancements could revolutionize the treatment landscape for a wide range of conditions, including hypertension, heart failure, and chronic pain.
Another area of potential breakthrough is the use of neuromodulation techniques to modulate the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. Researchers are exploring the use of electrical stimulation and other non-invasive techniques to regulate sympathetic nerve activity, offering a promising alternative to traditional pharmacological interventions. If successful, these approaches could provide a non-invasive and personalized treatment option for individuals with sympathetic nervous system disorders.
In conclusion, understanding the location, function, and disorders related to the sympathetic nervous system is crucial for comprehending human physiology. By delving into each aspect, we gain a comprehensive understanding of this complex system. Continued research in this field holds immense promise for improving medical treatments and advancing our knowledge of the intricate workings of the human body.