Pain management is a complex field that requires a deep understanding of the body’s intricate web of nerves and how they contribute to the perception and experience of pain. One such nerve, the lumbar sympathetic nerve, plays a crucial role in this process. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy, function, and potential pain management techniques involving the lumbar sympathetic nerve. It is important to note that while we aim to provide valuable insights, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.
Anatomy of the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve
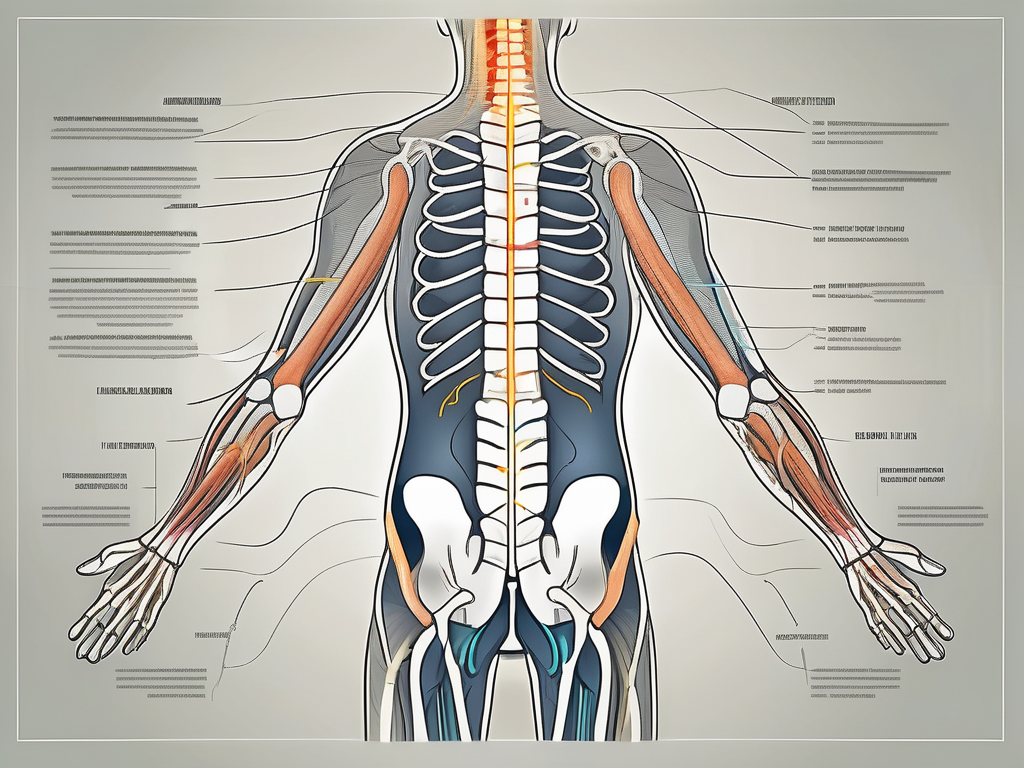
The lumbar sympathetic nerve is a fascinating component of the autonomic nervous system, which governs a wide range of involuntary bodily functions. It originates from the lumbar region of the spine, specifically the lower back, and extends downwards, branching out to various organs and tissues in the lower body. This nerve is composed of a complex network of fibers that transmit signals between the spinal cord and the targeted areas, allowing for seamless communication and regulation of physiological processes.
When we delve deeper into the location and structure of the lumbar sympathetic nerve, we discover its close proximity to the lumbar vertebrae, which are the five largest and strongest vertebrae in the lower back. Running parallel to these vertebrae, the lumbar sympathetic nerve forms an intricate pathway that ensures efficient transmission of signals. It consists of a series of ganglia, or nerve cell clusters, interconnected by nerve fibers. These ganglia play a crucial role in enabling the nerve to transmit and modulate signals effectively.
Now, let’s explore the multifaceted functions of the lumbar sympathetic nerve. One of its primary responsibilities is to regulate blood flow and control the distribution of nutrients to the lower limbs and organs. This intricate system ensures that vital organs and tissues receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, promoting optimal functioning. Additionally, the lumbar sympathetic nerve is involved in the regulation of sweating, a vital bodily function that helps regulate body temperature and maintain homeostasis.
Furthermore, the lumbar sympathetic nerve plays a significant role in the body’s response to stress. When we encounter a stressful situation, the nerve releases neurotransmitters that trigger the “fight or flight” response, preparing our body to either confront the threat or flee from it. This response involves various physiological changes, such as increased heart rate, heightened alertness, and dilation of blood vessels, all of which are orchestrated by the lumbar sympathetic nerve.
In conclusion, the lumbar sympathetic nerve is a remarkable component of the autonomic nervous system. Its intricate structure and location allow for efficient transmission of signals, enabling it to regulate blood flow, control nutrient distribution, regulate sweating, and play a crucial role in the body’s response to stress. Understanding the anatomy and functions of this nerve provides us with a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the human body and the intricate mechanisms that govern our physiological processes.
The Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve and Pain Perception
Understanding how the lumbar sympathetic nerve interacts with the sensation of pain is crucial for effective pain management strategies. Pain is a complex phenomenon that involves various physiological processes, and the lumbar sympathetic nerve plays a significant role in this intricate system.
The lumbar sympathetic nerve acts as a pathway for pain signals, carrying information from injured or inflamed tissues to the brain. When tissues are damaged, pain receptors activate and send signals to the nerve, which in turn relays these signals to the spinal cord and ultimately the brain, where pain is perceived.
However, the lumbar sympathetic nerve’s involvement in pain perception goes beyond being a mere messenger. It also has the ability to influence the intensity of pain experienced. This modulation occurs through the release of certain neurotransmitters that affect the sensitivity of pain receptors.
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells. In the case of the lumbar sympathetic nerve, the release of specific neurotransmitters can either amplify or attenuate the perception of pain. For example, the release of norepinephrine can enhance the sensitivity of pain receptors, making the pain feel more intense. On the other hand, the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers, can dampen the pain signals and provide relief.
Understanding the intricate interplay between the lumbar sympathetic nerve and pain perception is essential for developing effective pain management strategies. Medical professionals often utilize various techniques to target this nerve and modulate its activity to alleviate pain. These techniques may include nerve blocks, where medication is injected near the lumbar sympathetic nerve to block its function temporarily.
Moreover, research is ongoing to explore the potential of targeting the lumbar sympathetic nerve for pain relief. Scientists are investigating novel approaches, such as neuromodulation techniques, to selectively stimulate or inhibit this nerve’s activity. These advancements hold promise for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions, offering new avenues for managing their symptoms.
In conclusion, the lumbar sympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in pain perception. It acts as a pathway for pain signals and also has the ability to modulate the intensity of pain experienced. By understanding the intricate mechanisms involved in this process, medical professionals can develop more effective pain management strategies and provide relief to those in need.
Pain Management Techniques Involving the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve
When it comes to managing pain associated with the lumbar sympathetic nerve, various non-surgical and surgical interventions can be considered. However, each individual’s situation and medical history are unique, and it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
The lumbar sympathetic nerve plays a vital role in transmitting pain signals from the lower back to the brain. When this nerve becomes irritated or damaged, it can result in chronic pain that significantly affects an individual’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are several techniques available to manage this type of pain, ranging from non-surgical interventions to surgical approaches.
Non-Surgical Interventions for Pain Management
Non-surgical interventions for lumbar sympathetic nerve pain management primarily focus on conservative measures. These may include physical therapy, medication, nerve blocks, and other minimally invasive procedures that aim to alleviate pain symptoms without surgical intervention. Physical therapy, for example, can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the lumbar sympathetic nerve, providing support and reducing strain on the affected area.
Medication is another non-surgical approach commonly used to manage pain associated with the lumbar sympathetic nerve. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain, while muscle relaxants can help ease muscle spasms that often accompany this condition.
In some cases, nerve blocks may be recommended to provide temporary pain relief. This procedure involves injecting a local anesthetic or a combination of anesthetics and steroids into the affected area to block the transmission of pain signals. Nerve blocks can provide immediate relief and allow individuals to engage in physical therapy or other rehabilitative measures more effectively.
Other minimally invasive procedures, such as radiofrequency ablation, may also be considered. This technique uses heat generated by radio waves to destroy the nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals. By targeting the lumbar sympathetic nerve, radiofrequency ablation can provide long-lasting pain relief for individuals who have not responded well to other non-surgical interventions.
Surgical Approaches to Pain Management
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address lumbar sympathetic nerve-related pain. Surgical options may include sympathectomy, a procedure that involves cutting or damaging certain nerves to interrupt the transmission of pain signals. Sympathectomy can be performed through open surgery or minimally invasive techniques, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health.
During an open sympathectomy, the surgeon makes an incision in the lower back to access the lumbar sympathetic nerve. The damaged or irritated portions of the nerve are then removed or cut to disrupt the pain signals. Minimally invasive techniques, such as endoscopic sympathectomy, involve smaller incisions and the use of specialized instruments to access and treat the affected nerve.
It is essential to note that surgical interventions carry risks, and the decision to proceed should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional. Factors such as the individual’s overall health, the severity of the pain, and the potential benefits and risks of surgery should all be carefully considered before making a decision.
In conclusion, managing pain associated with the lumbar sympathetic nerve requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the individual’s unique circumstances. Non-surgical interventions, such as physical therapy, medication, nerve blocks, and minimally invasive procedures, can provide significant relief for many individuals. However, in cases where non-surgical options are not effective, surgical approaches like sympathectomy may be considered. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most appropriate pain management technique for each individual.
Risks and Benefits of Targeting the Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve
Before deciding on any pain management technique involving the lumbar sympathetic nerve, it is crucial to consider the potential risks and benefits associated with such interventions.
Potential Side Effects and Complications
As with any medical procedure, there are potential side effects and complications associated with interventions targeting the lumbar sympathetic nerve. These may include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, or unintended adverse effects. Understanding the potential risks and discussing them with a healthcare professional is imperative before making an informed decision.
Efficacy and Patient Outcomes
Evaluating the efficacy of pain management techniques involving the lumbar sympathetic nerve is essential. Individuals may experience varying outcomes depending on factors such as the underlying condition, overall health, and response to treatment. Healthcare professionals can provide insight into the likelihood of successful pain relief and potential improvements in quality of life based on their experience and expertise.
Future Directions in Lumbar Sympathetic Nerve Research
Continued research into the lumbar sympathetic nerve holds promise for advancements in pain management techniques and understanding its role in various conditions. Ongoing studies explore emerging therapies and techniques that aim to enhance outcomes for individuals experiencing lumbar sympathetic nerve-related pain.
Emerging Therapies and Techniques
Scientists and medical professionals are constantly investigating novel approaches to managing pain associated with the lumbar sympathetic nerve. These include advancements in nerve stimulation techniques, pharmacological interventions, and targeted therapies that aim to provide precise and effective pain relief. Monitoring scientific publications and consulting with healthcare professionals can provide updates on these emerging treatments.
Unanswered Questions and Areas for Further Study
While significant progress has been made in understanding the role of the lumbar sympathetic nerve in pain management, there are still unanswered questions and areas for further study. Ongoing research seeks to uncover additional mechanisms, potential therapeutic targets, and refine existing techniques to optimize pain management strategies further.
In conclusion, the lumbar sympathetic nerve plays a vital role in pain perception and can be targeted for pain management interventions. Understanding its anatomy, function, and potential treatment options is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking effective pain relief. However, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action based on individual circumstances and to navigate the complex landscape of pain management successfully.