The sacral sympathetic nerve is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system, playing a significant role in various bodily functions. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential disorders is essential for comprehensive medical knowledge. In this guide, we will delve into the intricate details of the sacral sympathetic nerve, shedding light on its significance in pain management and paving the way for future research.
Anatomy of the Sacral Sympathetic Nerve
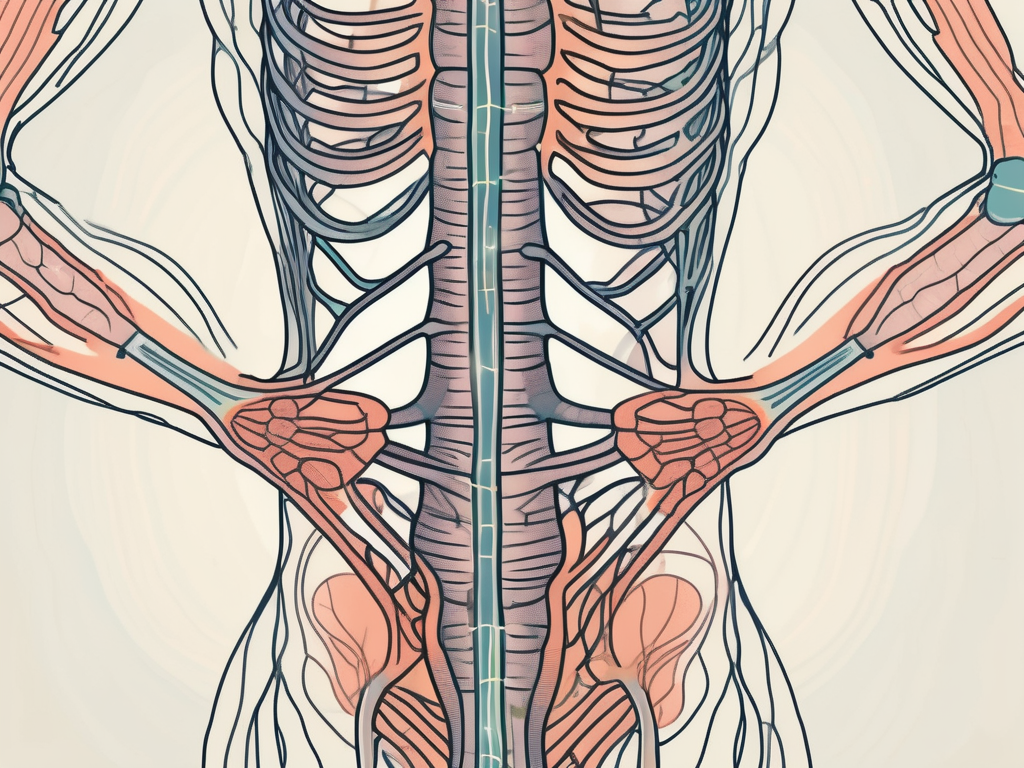
The sacral sympathetic nerve is located within the sacrum, a triangular bone situated at the base of the spine. It consists of a series of ganglia, interconnected nerve bundles that extend from the spinal cord. These ganglia form a complex network known as the sacral sympathetic chain. Each ganglion plays a distinct role in transmitting nerve signals to various body parts.
The sacral sympathetic nerve is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily processes. It works in conjunction with other nerves and structures to regulate functions such as heart rate, digestion, and sexual response. The sacral sympathetic nerve specifically focuses on innervating the pelvic organs, lower limbs, and genitalia, ensuring their proper function and coordination.
Within the sacral sympathetic chain, the ganglia are strategically positioned to facilitate efficient communication between the central nervous system and the targeted body parts. These ganglia serve as relay stations, receiving signals from the brain and spinal cord and transmitting them to the appropriate destinations. This intricate network allows for precise control and coordination of the various physiological processes influenced by the sacral sympathetic nerve.
Location and Structure of the Sacral Sympathetic Nerve
The sacral sympathetic nerve starts in the lower thoracic region of the spinal cord and extends down to the sacrum. It is a bilateral structure, meaning it exists on both sides of the spinal column. This bilateral arrangement ensures symmetrical innervation and coordination of the pelvic organs, lower limbs, and genitalia.
The nerve fibers within the sacral sympathetic nerve are bundled together, forming distinct pathways that travel along the sacrum. These pathways are protected by layers of connective tissue and surrounded by blood vessels, ensuring their integrity and nourishment. The structure of the sacral sympathetic nerve reflects its vital role in maintaining proper physiological function throughout the body.
As the nerve extends from the spinal cord to the sacrum, it branches out into smaller nerve fibers, reaching various target organs and tissues. These branches allow for specific and localized control of different body parts, ensuring that each receives the appropriate nerve signals for optimal functioning.
Connection to the Central Nervous System
The sacral sympathetic nerve is an integral part of the autonomic nervous system, which operates independently of conscious control. It connects with the central nervous system, comprising the brain and spinal cord, through specialized nerve fibers.
These nerve fibers serve as a communication pathway between the brain, spinal cord, and the sacral sympathetic nerve. They transmit signals in both directions, allowing the central nervous system to regulate and modulate the activity of the sacral sympathetic nerve, while also receiving feedback from the targeted body parts.
Through this intricate connection, the central nervous system can influence the functioning of the sacral sympathetic nerve, adjusting its activity based on the body’s needs and external stimuli. This bidirectional communication ensures that the body can respond appropriately to various situations, maintaining homeostasis and adapting to changing conditions.
In summary, the sacral sympathetic nerve is a complex and vital component of the autonomic nervous system. Its location within the sacrum, intricate structure, and connection to the central nervous system allow for precise control and coordination of the pelvic organs, lower limbs, and genitalia. Understanding the anatomy and function of the sacral sympathetic nerve provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying various physiological processes in the human body.
Functions of the Sacral Sympathetic Nerve
The sacral sympathetic nerve plays a vital role in regulating the autonomic nervous system. Its functions span numerous bodily processes, ensuring their proper functionality and coordination.
The sacral sympathetic nerve, also known as the sacral part of the sympathetic trunk, is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system. It is responsible for maintaining homeostasis, the body’s internal balance, by working in conjunction with the parasympathetic nervous system. Together, these two systems regulate vital functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and respiration. This intricate interplay allows the body to respond and adapt to external and internal stimuli, ensuring optimal functioning.
One of the significant impacts of the sacral sympathetic nerve is its influence on sexual function. It plays a crucial role in controlling the timing and intensity of both male and female reproductive processes. In males, it helps regulate the erection and ejaculation processes, ensuring successful sexual intercourse. In females, it contributes to the regulation of the menstrual cycle and the coordination of various reproductive events, such as ovulation and fertilization.
Furthermore, the sacral sympathetic nerve is involved in bladder control. It regulates the relaxation and constriction of the bladder’s smooth muscles, ensuring efficient urine storage and elimination. This coordination is essential for maintaining proper bladder function and preventing urinary incontinence.
Additionally, the sacral sympathetic nerve has been found to have an impact on other bodily functions. It has been linked to the regulation of blood flow to the lower extremities, contributing to the control of blood pressure. Moreover, it plays a role in the modulation of pain signals, providing relief in certain pain conditions.
Overall, the sacral sympathetic nerve is a multifaceted component of the autonomic nervous system. Its functions extend beyond the regulation of basic bodily processes, influencing sexual function, bladder control, blood flow, and pain modulation. Understanding the intricate workings of this nerve is crucial for comprehending the complexity of the human body and its ability to maintain homeostasis.
Disorders Related to the Sacral Sympathetic Nerve
Like any other component of the nervous system, the sacral sympathetic nerve can be affected by disorders that disrupt its normal functioning. Being aware of these disorders, their symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for comprehensive medical care.
The sacral sympathetic nerve, also known as the sacral autonomic nerve, plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions. It is responsible for controlling the sympathetic nervous system in the sacral region, which includes the pelvic organs and structures. When this nerve is affected by disorders, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
Disorders related to the sacral sympathetic nerve may manifest as various symptoms, including pelvic pain, urinary dysfunction, sexual dysfunction, and bowel irregularities. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and require prompt medical attention.
Diagnosing disorders related to the sacral sympathetic nerve can be challenging, as the symptoms may overlap with other conditions. A thorough medical history evaluation is crucial in understanding the onset and progression of symptoms. Additionally, physical examinations, including neurological assessments, can help identify any abnormalities. In some cases, imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, may be necessary to visualize the affected area. Specialized tests, such as urodynamic studies or electromyography, may also be performed to assess the function of the pelvic organs and muscles.
Treatment Options and Prognosis
When dealing with disorders involving the sacral sympathetic nerve, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional. The treatment options may vary based on the specific condition and its severity.
Medication can be prescribed to manage symptoms and alleviate pain. Different classes of medications, such as analgesics, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants, may be used to target specific symptoms and improve overall function.
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the management of disorders related to the sacral sympathetic nerve. Therapeutic exercises and techniques can help strengthen the pelvic muscles, improve bladder and bowel control, and alleviate pain. Additionally, biofeedback training may be utilized to enhance awareness and control of pelvic floor muscles.
In some cases, nerve blocks may be recommended to provide temporary relief from pain and other symptoms. These blocks involve the injection of local anesthetics or steroids near the affected nerves to interrupt pain signals and reduce inflammation.
In severe cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options may include nerve decompression, neuromodulation, or even nerve grafting in certain situations. These procedures aim to alleviate pressure on the affected nerves or restore their function.
The prognosis for disorders related to the sacral sympathetic nerve depends on various factors, including the underlying cause, the timeliness of intervention, and the individual’s overall health. With proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and regain a better quality of life.
The Sacral Sympathetic Nerve and Pain Management
Understanding the relationship between the sacral sympathetic nerve and chronic pain can provide insights into effective pain management strategies.
Understanding Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is persistent pain that lasts beyond the normal healing process. It can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life and overall well-being. By identifying the involvement of the sacral sympathetic nerve in chronic pain conditions, healthcare professionals can tailor treatments to alleviate patient discomfort.
Role of the Sacral Sympathetic Nerve in Pain Perception
The sacral sympathetic nerve can contribute to pain perception and modulation mechanisms. Dysfunction within this nerve network may lead to abnormal pain processing, resulting in increased sensitivity to painful stimuli or chronic pain conditions. In these cases, interventions targeting the sacral sympathetic nerve may offer potential relief.
Future Research Directions in Sacral Sympathetic Nerve Study
Despite significant advancements in understanding the sacral sympathetic nerve, several aspects remain unexplored. Future research endeavors hold the potential to deepen our knowledge and facilitate advancements in medical care.
Current Limitations in Understanding
While the sacral sympathetic nerve’s role in various bodily functions and pain management is acknowledged, there are still limitations in our understanding of its precise mechanisms. Further research is needed to elucidate the intricate connections and signaling pathways within this nerve network.
Potential Areas for Future Exploration
Future research should focus on identifying novel therapeutic targets and interventions that specifically target the sacral sympathetic nerve. Additionally, studies on the interaction between the sacral sympathetic nerve and other components of the nervous system could provide insights into broader physiological responses and potential treatment avenues.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the sacral sympathetic nerve is crucial for medical professionals in providing effective care and managing various conditions. By exploring its anatomy, functions, potential disorders, and implications in pain management, we pave the way for further research and advancements in the field. Consultation with healthcare professionals is recommended for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and personalized care.